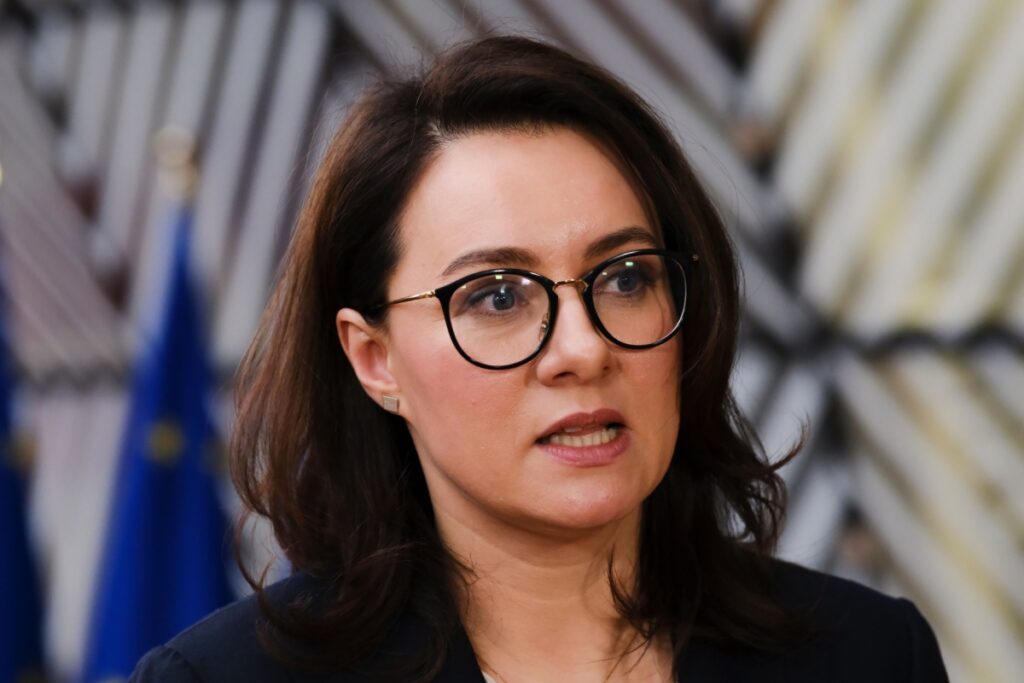
Ukraine’s government has presented its draft budget for 2026, outlining a deficit equivalent to 18.4% of gross domestic product (GDP), Prime Minister Yulia Svyrydenko announced. The budget envisions revenues of around 2.8 trillion hryvnias (approximately USD 67 billion) against expenditures projected at 4.8 trillion hryvnias. The gap underscores the scale of fiscal pressures facing Ukraine as it continues to fund defence, social programs, and post-war reconstruction efforts.
The proposal represents one of the largest peacetime deficits in modern Ukrainian history, reflecting extraordinary conditions created by the ongoing conflict with Russia. The budget will now be submitted to parliament, where lawmakers are expected to debate its priorities and financing strategies in the coming months.
Balancing Defence and Social Spending
A substantial share of the 2026 spending plan is directed towards defence and security, which remain central priorities as the war continues into its fourth year. Officials noted that funding will cover military procurement, soldier salaries, and logistical support, ensuring the country can sustain its defensive operations.
At the same time, the government pledged to preserve financing for pensions, healthcare, and education, sectors heavily affected by wartime disruption. Reconstruction of damaged infrastructure, including housing, roads, and energy facilities, is also a core component. This dual emphasis illustrates the challenge of allocating limited resources to immediate military needs while laying groundwork for long-term recovery.
Reliance on International Partners
The projected shortfall highlights Ukraine’s ongoing dependence on international assistance. Since 2022, the country has received tens of billions of dollars in aid from partners such as the European Union, the United States, and institutions like the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank.
Prime Minister Svyrydenko emphasized that continued external financing will be essential for bridging the budget gap. The government has pledged transparency in its spending to reassure lenders and donors. International institutions have stressed the importance of fiscal discipline and reform to maintain credibility, even as Ukraine grapples with extraordinary wartime needs.
Economic Pressures and Inflation Risks
Ukraine’s economy has shown signs of resilience, with modest growth reported in 2024 and early 2025, supported by agricultural exports and foreign aid. However, the enormous financing needs raise concerns about debt sustainability and inflation. The National Bank of Ukraine has already warned of risks linked to heavy government borrowing and currency instability.
Inflation, which eased to around 7% in mid-2025 after spiking during the early war years, could accelerate if fiscal deficits are not carefully managed. The government is expected to explore measures to expand the domestic tax base, improve customs efficiency, and combat corruption to boost revenues.
Outlook for Parliamentary Review
Parliament is set to begin reviewing the draft in October, with debates likely to focus on how to prioritize spending, secure additional financing, and safeguard economic stability. Analysts expect significant amendments before final approval, as lawmakers seek to balance urgent military requirements with public demands for social support.
The 2026 budget is being watched closely by international lenders, who view it as a test of Ukraine’s ability to manage its finances under wartime conditions. For Kyiv, the plan represents both a roadmap for survival and a statement of intent to maintain governance despite unprecedented challenges.