A New Framework Reshapes Arctic Security
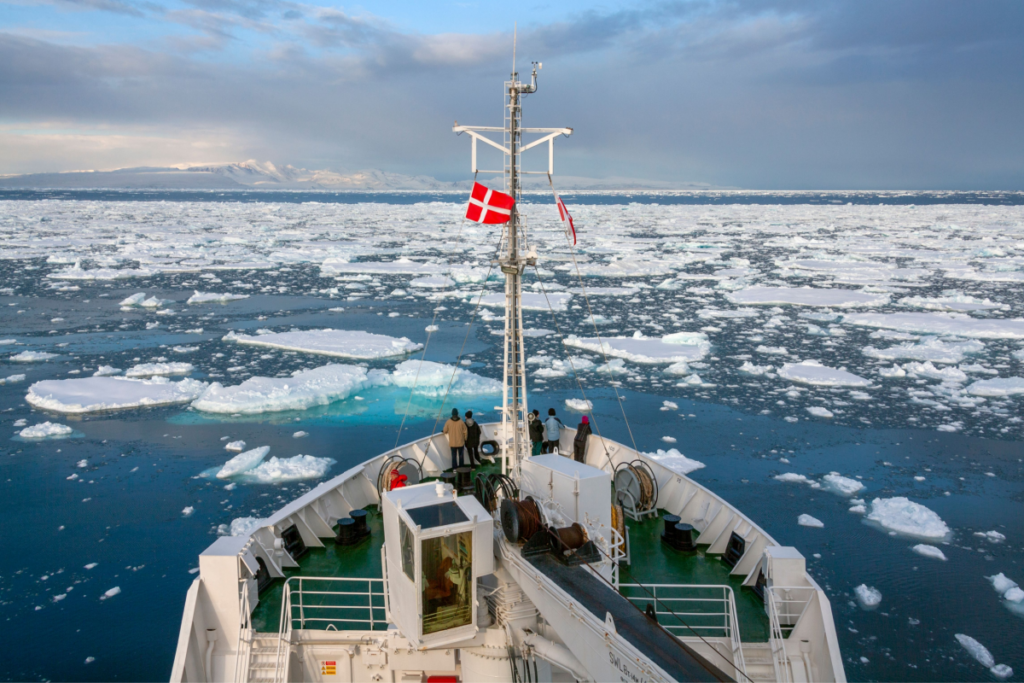
The United States is moving toward what President Donald Trump has described as a sweeping security arrangement granting Washington total access to Greenland, including the ability to establish and expand military bases across the Arctic island. The framework, still under negotiation, is presented by the US administration as a strategic breakthrough that delivers unrestricted military presence, long-term security guarantees, and broad operational freedom at no financial cost to the United States.
Under this emerging arrangement, the US would secure permanent access with no fixed end date for its military footprint. The deal is framed as essential to safeguarding Arctic security interests and extending advanced defense coverage over the region, including integration with the Golden Dome air defense system. While formal sovereignty over Greenland remains uncertain, US officials emphasize that operational control and access are the primary objectives, not immediate territorial acquisition.
Strategic Access Without Formal Ownership
The administration has signaled that formal ownership of Greenland may not be necessary to achieve its goals. While the possibility of future acquisition has not been ruled out, the current focus is on securing comprehensive military and security rights. The approach marks a shift from earlier rhetoric centered on outright acquisition toward a more pragmatic security-driven framework.
From Washington’s perspective, the arrangement ensures full strategic reach in the Arctic without triggering the diplomatic and legal complexities of territorial transfer. The US would gain the ability to build, operate, and expand military installations as needed, while maintaining freedom of movement and long-term defense planning capabilities. This model allows the US to strengthen its Arctic posture amid rising global competition in the region.
The announcement of the framework was also followed by a positive reaction in financial markets, which rebounded after earlier volatility linked to trade tensions and geopolitical uncertainty. The administration has portrayed this response as evidence that investors view the emerging security deal as stabilizing and strategically beneficial.
Denmark and Allies Respond With Cautious Relief
The government of Denmark, which retains sovereignty over Greenland, reacted with measured relief following the clarification that military force would not be used to seize the territory. Danish officials emphasized the importance of addressing US security concerns while respecting national sovereignty and established legal boundaries.
Denmark and the United States are already bound by a longstanding defense agreement that permits US defense areas in Greenland with Danish approval. That agreement allows the US to improve and adapt facilities for military use in cooperation with Danish authorities. It remains unclear how the new framework would expand upon or modify these existing provisions, though the current negotiations appear aimed at significantly broadening US operational autonomy.
The announcement also eased broader tensions with European partners, as the US administration stepped back from previously threatened trade measures. The recalibration was welcomed by European leaders, who see dialogue and negotiation as preferable to escalation, particularly in a region as strategically sensitive as the Arctic.
Arctic Security and the Global Balance
The renewed focus on Greenland reflects the growing importance of the Arctic in global security calculations. Melting ice, emerging shipping routes, and increased competition among major powers have elevated the region’s strategic value. The US argues that its expanded presence will enhance collective security and deter rival powers seeking influence in the Arctic.
The framework discussed with allies, including NATO, is positioned as a contribution to broader transatlantic security. By strengthening surveillance, missile defense coverage, and rapid deployment capabilities, the US aims to reinforce what it describes as a strained international security system.
At the same time, critics question the long-term implications of granting open-ended military access without clear oversight mechanisms. The absence of defined time limits or explicit constraints raises concerns about balance between security needs and sovereignty. These issues are expected to remain central as negotiations continue and details are refined.
What is clear is that Greenland has moved to the center of global strategic planning. Whether the final agreement results in formal changes to existing treaties or simply expands their interpretation, the Arctic island is set to play a pivotal role in the evolving security architecture of the North Atlantic and beyond.