Economic Stimulus Amid Trade Pressures
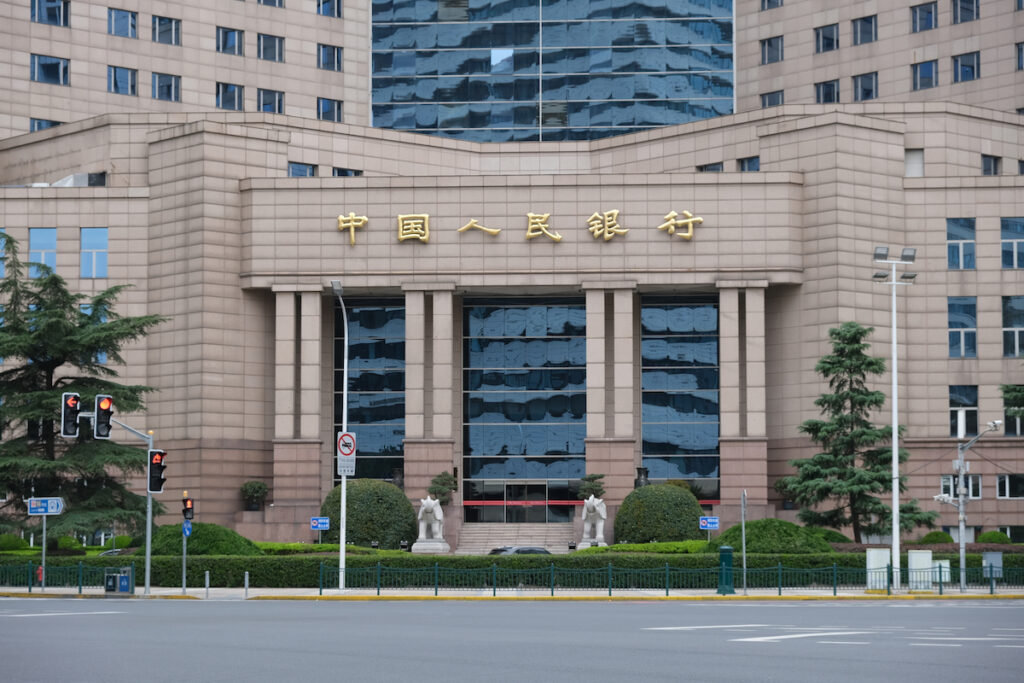
In response to mounting economic challenges exacerbated by a trade war with the United States, China has unveiled a series of monetary stimulus measures aimed at bolstering its slowing economy. The People’s Bank of China (PBOC) announced cuts to key interest rates and reduced bank reserve requirements, effectively injecting approximately 1 trillion yuan ($137.6 billion) into the financial system. These steps are designed to support sectors such as manufacturing upgrades, technological innovation, and elder care services.
The Chinese economy, heavily reliant on exports, has been significantly impacted by U.S. tariffs reaching up to 145% on Chinese goods . In retaliation, China imposed tariffs up to 125% on U.S. imports and ceased purchases of American agricultural products. Despite public declarations of resilience, both nations have agreed to resume trade negotiations in Geneva later this week.
Diverging Economic Indicators
China reported a 5.4% economic growth in the first quarter of 2025; however, analysts question the accuracy of this figure amid declining export orders and waning business confidence . Conversely, the U.S. economy contracted by 0.3% during the same period, marking the first decline in three years . The contraction is attributed to a surge in imports as companies rushed to procure goods ahead of tariff implementations, coupled with a slowdown in consumer spending.
Financial markets have responded with caution. While initial gains were observed in Hong Kong and Shanghai, these were short-lived. In the U.S., Wall Street exhibited mixed performance, with the S&P 500 remaining mostly flat, the Dow Jones Industrial Average rising by 147 points (0.4%), and the Nasdaq Composite falling by 0.3%.
Policy Responses and Market Reactions
The Federal Reserve faces a complex balancing act as it navigates the economic implications of the ongoing trade war. Despite President Trump’s calls for immediate rate cuts to stimulate growth, the Fed has signaled a cautious approach, opting to monitor the effects of tariffs on inflation and the broader economy before making any adjustments . The uncertainty stemming from fluctuating trade policies has led businesses to delay investments and hiring, potentially slowing economic growth and increasing unemployment.
Meanwhile, China’s central bank’s recent actions aim to buffer its exporters and provide economic stability during negotiations. Economists, however, warn that easing monetary policy may not sufficiently boost demand, suggesting that broader fiscal interventions might be necessary.
Prospects for Resolution
The upcoming trade talks in Geneva represent a critical juncture in the U.S.-China economic relationship. While both sides have expressed a willingness to engage in dialogue, significant differences remain. China’s Commerce Ministry emphasized that any discussions would be grounded in mutual respect and equality, reaffirming that it will not compromise its principles .
As the global economy grapples with the ramifications of this trade conflict, the outcomes of these negotiations will be closely watched by markets and policymakers worldwide. A lasting resolution remains uncertain, but the resumption of talks offers a glimmer of hope for de-escalation and renewed economic cooperation.